Introduction
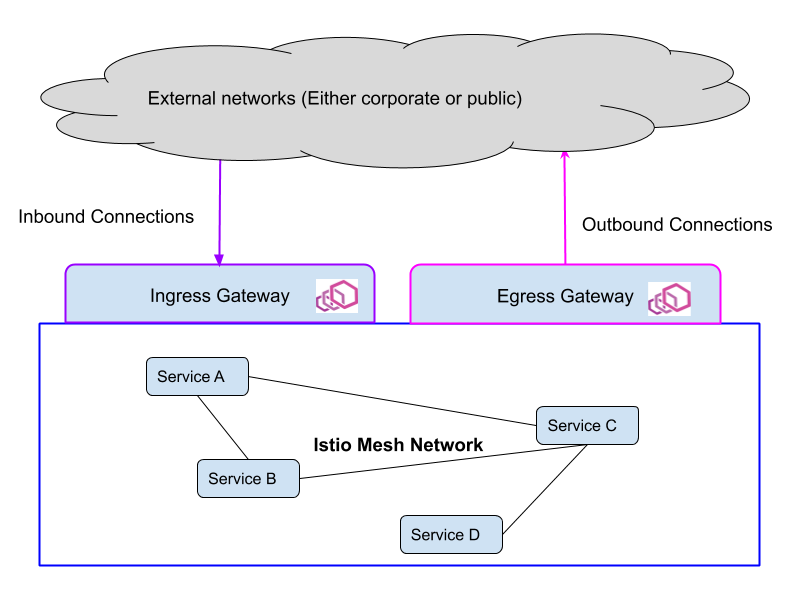
An Istio Gateway describes a load balancer operating at the edge of the mesh receiving incoming or outgoing HTTP/TCP connections. The specification describes a set of ports that should be exposed, the type of protocol to use, virtual host name to listen to, etc.
Ingress enables expose services to the external world and thus it is the entry point for all service running within the mesh.
Istio Gateway is based on envoy proxy, it handle reverse proxy and load balancing for services running in the service mesh network.
Istio Gateway vs Kubernetes Gateway
Unlike Kubernetes Ingress Resources, Istio Ingress does not include any traffic routing configuration. Traffic routing for ingress traffic is instead configured using Istio routing rules, exactly in the same was as for internal service requests.
How it works
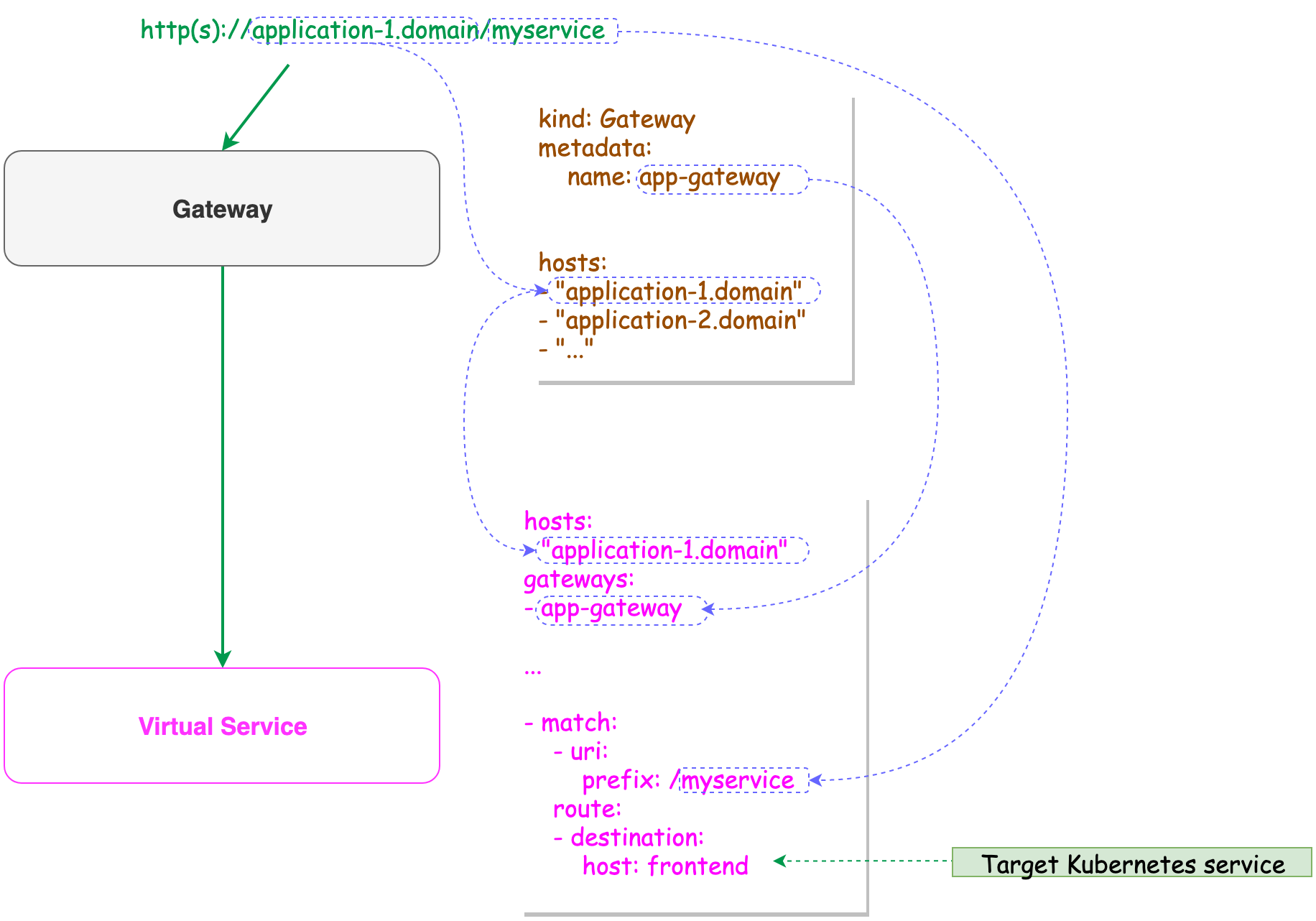
The Ingress Resource is handled by two Istio Resources:
| Resource | API | Version |
|---|---|---|
| Gateway | networking.istio.io | v1alpha3 |
| VirtualService | networking.istio.io | v1alpha3 |
Gateway: The Gateway resource is used to configure hosts exposed by the Gateway.
Valid protocols are:HTTP|HTTPS|GRPC|HTTP2|MONGO|TCP|TLS. More info about Gateways can be found in the Istio Gateway docs.
Virtual Service: VirtualService works in tandem with the Gateway. it defines the destination service. A Virtual Service defines the rules that control how requests for a service are routed within an Istio service mesh (Mesh Network). For example, a virtual service can route requests to different versions of a service or to a completely different service than was requested. Requests can be routed based on the request source and destination, HTTP paths and header fields, and weights associated with individual service versions.
When a VirtualService is configured with a Gateway resource using gateways field. This is means that the service is exposed to outside of the mesh network. If not the service is mesh-wide only.
Define an Ingress resource
Actually, The Hispter commerce application is exposed to external world using a Kubernetes Controller LoadBalancer provided by the Cloud Provider:
Delete the LoadBalancer service:
kubectl delete service frontend-externalFirst, we need to find the Istio Ingress IP address:
export INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}' -n istio-system) echo $INGRESS_IPConnect to the Istio Ingress IP:
curl $INGRESS_IPcurl: (7) Failed to connect to 35.187.106.238 port 80: Connection refused
The connection is refused because no service is running behind the ingress gateway.
Let’s create a Gateway to the Hipster application so the application will be exposed to the external world through the Mesh Ingress Gateway but before that let’s configure Cloud DNS to associate our domain name to the Ingress Gateway:
On Google Cloud dashboard menu, select Network services → Cloud DNS then edit the zone created previously:
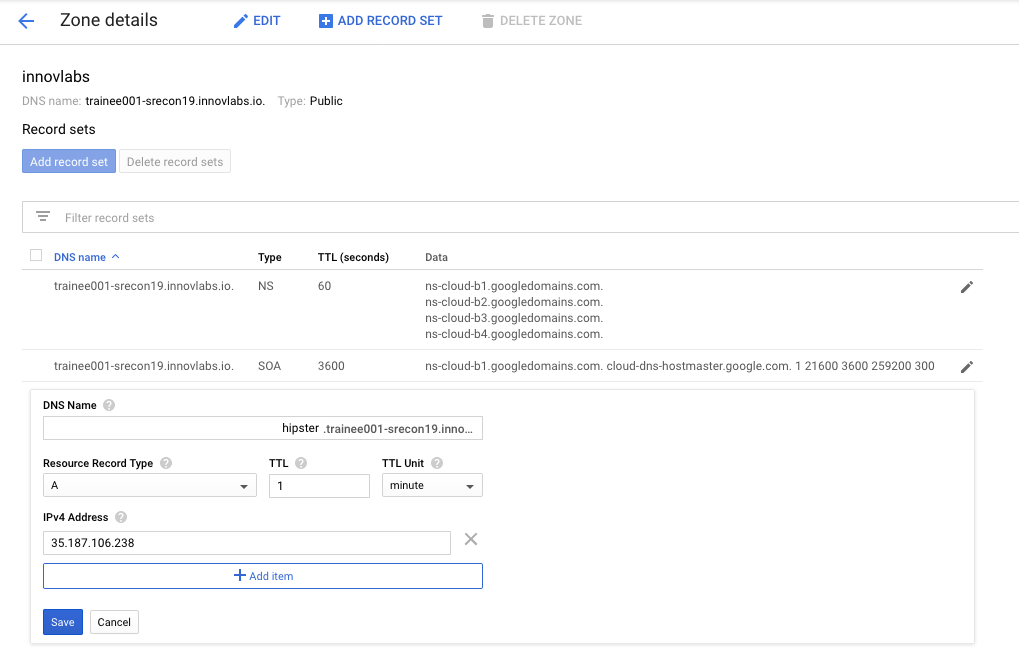 Update the IPv4 Address with the value of
Update the IPv4 Address with the value of $INGRESS_IPthen click save.We need to create a Gateway resource and Virtual Service:
Please change the host name in
$WORKSHOP_HOME/istio-workshop-labs/frontend-ingress.yamlwith your own before running the command.kubectl apply -f $WORKSHOP_HOME/istio-workshop-labs/frontend-ingress.yamlCheck that the gateway and and the virtual service are created:
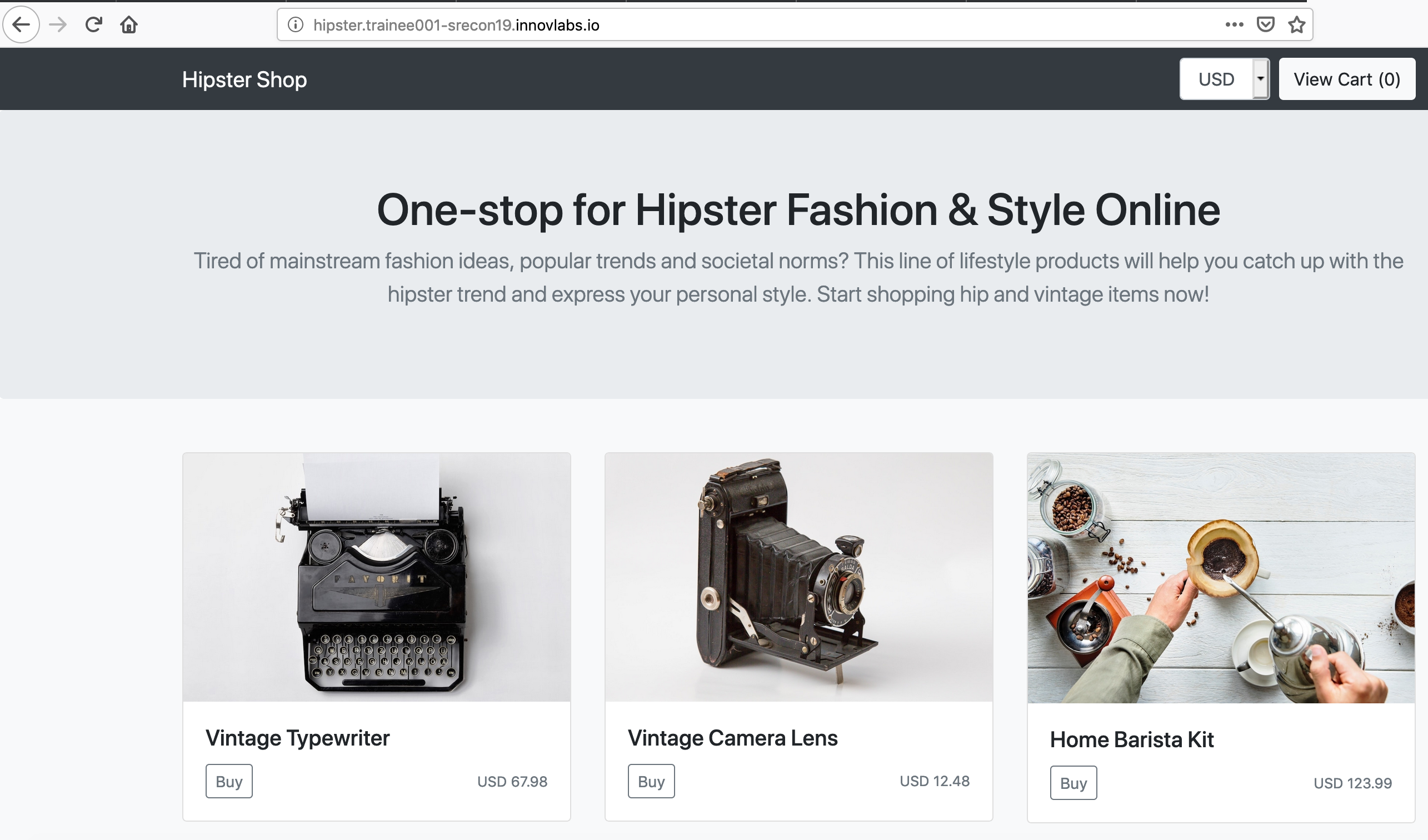
kubectl get virtualservice,gatewayNAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE virtualservice.networking.istio.io/hispter [app-gateway] [hipster.trainee001-srecon19.innovlabs.io] 5h NAME AGE gateway.networking.istio.io/app-gateway 5hCheck the application on the browser using the configured host:
Exercise:
let’s assume that we want to expose Istio dashbaord using Ingress Gateway as following:
dashboard.your-domain-srecon19.innovlabs.io/kiali → Kiali
tracing.your-domain-srecon19.innovlabs.io → Jaeger Tracing
Create a YAML file that create an ingress resource for one of these Addons and deploy it to the mesh.
Don’t forget the prefix ;)